What do alcohol use disorder (AUD) and schizophrenia have to do with each other? Chances are that you have met a person suffering from both conditions. You may know this person in your personal life, or perhaps have come across them living on the street. Unfortunately, this dual diagnosis can be devastating to a person’s wellbeing and lifestyle, which is why they may struggle functionally and financially.
AUD and schizophrenia might seem like separate issues, but there is actually a deep connection between. Research shows that individuals with schizophrenia are more likely to struggle with AUD, which can lead to more severe symptoms and make recovery even harder. For those affected, managing both conditions can feel like an uphill battle.
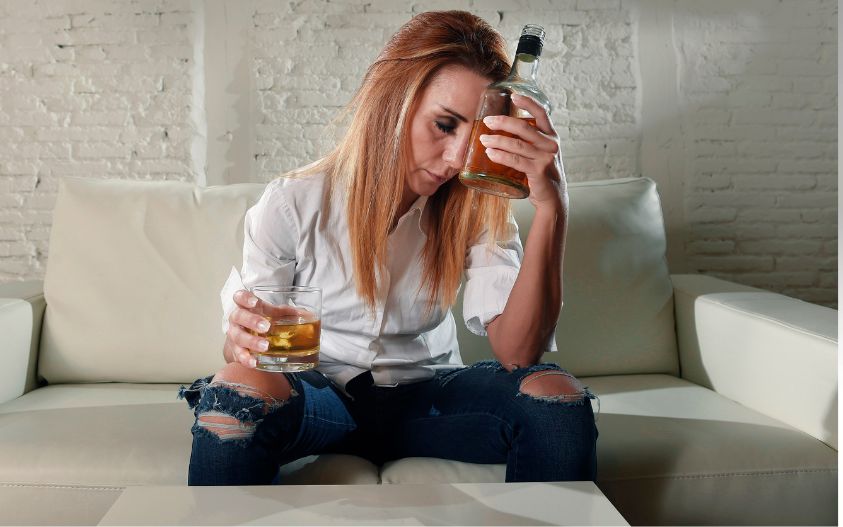

People with both AUD and schizophrenia can display symptoms that are difficult for loved ones to manage, leading to scenarios in which they do not receive the sympathy and help that they need. It is important to better understand the connection between AUD and schizophrenia so as to dispel the stigma and make it easier for those suffering, as well as their loved ones, to seek the right treatment.
What do I Need to Know About Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) and Schizophrenia?
Both alcohol use disorder (AUD) and schizophrenia are mental illnesses that are subject to dangerous misconceptions. While AUD is often seen by society as a moral failing, it is in fact a chronic mental health condition. A person with AUD struggles to control alcohol consumption despite negative consequences and even the knowledge that it is destroying their life.
Some of the most common symptoms of AUD include physical dependence on alcohol, withdrawal, and a compulsive need to drink. It is both a physical and mental health condition. People with AUD commonly battle depression, anxiety, and impaired cognitive function. Although most people assume they stand no chance of becoming addicted, the disorder has strong genetic components and cannot be avoided through willpower alone.
What about schizophrenia? In the past, misrepresentations in the media led to a widespread belief that people with schizophrenia had split personalities. Fortunately, this misconception is no longer as prevalent, but inaccurate beliefs still remain.
Schizophrenia is a severe and chronic mental health disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. Its common symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and reduced emotional expression. While the exact cause of schizophrenia remains unknown, genetic and neurobiological factors play a significant role, as do environmental triggers like stress or substance abuse. Together, these conditions can create a complex and debilitating combination.
What is The Connection Between AUD and Schizophrenia?
Research has long shown that the connection between AUD and schizophrenia exists. Studies suggest that individuals with schizophrenia are up to three times more likely to develop AUD compared to the general population. But why should this be?
The connection between these two disorders is caused by several shared risk factors, including genetic vulnerabilities, early life trauma, and environmental stressors.
One major factor in this connection is the concept of self-medication. Many people with schizophrenia turn to alcohol as a way to cope with symptoms such as hallucinations or anxiety. Unfortunately, although it may seem to provide temporary relief, alcohol often exacerbates these symptoms, leading to a vicious cycle of dependency and worsening mental health. For example, alcohol can intensify paranoia or interfere with medications prescribed to manage schizophrenia.
Neurobiological factors also play a role. Both conditions are associated with disruptions in the brain’s dopamine system, which affects reward, motivation, and emotional regulation. This overlap may explain why some individuals are particularly vulnerable to developing both disorders.
What Challenges Exist in the Diagnosis and Treatment of AUD and Schizophrenia?
When AUD and schizophrenia occur together, diagnosing and treating these conditions becomes more challenging. One of the biggest hurdles is the overlapping symptoms. For instance, alcohol withdrawal can mimic psychotic episodes, making it difficult to determine whether the symptoms are related to schizophrenia or alcohol use. Similarly, the cognitive impairments caused by AUD can obscure the severity of schizophrenia symptoms.
Another major challenge is stigma. People struggling with co-occurring AUD and schizophrenia often face judgment and misunderstanding from both society and healthcare providers. This stigma can prevent them from seeking help or receiving adequate care. Furthermore, traditional treatment models often address these conditions separately, failing to consider their interconnected nature.
Dual diagnosis or integrated care is crucial, but it is not always accessible, especially in areas where mental healthcare is lacking. When there is no collaboration between mental health and addiction treatment providers, the person is left without the comprehensive support they need.
How is Co-Occurring AUD and Schizophrenia Treated?
Effective treatment for individuals with both AUD and schizophrenia requires a holistic, integrated approach. This begins with a thorough assessment to identify the severity of both conditions and tailor a treatment plan accordingly.
Medications
Medications can play a key role in managing both disorders but are particularly important in treating schizophrenia. Antipsychotic drugs help control schizophrenia symptoms which otherwise may make it impossible for the person to function. With regards to AUD, medications like naltrexone or acamprosate can help reduce alcohol cravings or lessen the challenges of withdrawal. It is important that the potential interactions between AUD and schizophrenia medications are taken into account.
Therapy
Multiple therapies are useful for managing both disorders. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) in particular has proven effective for addressing negative thought patterns and improving coping strategies. Group therapy is crucial in addiction recovery and can also help people with schizophrenia to feel less alone.
Dual Diagnosis Rehab Programs
Rehabs that are committed to dual diagnosis programs are necessary to provide a structured environment for the person to recover, as well as the custom approach they need. A dual diagnosis program will include psychiatric treatment, therapy, life skills training, and relapse prevention strategies.
Holistic Approaches
Both conditions affect the person physically and mentally and thus require holistic approaches. People with AUD and schizophrenia may struggle with nutrition, and require help in creating meal plans. Mindfulness practices have proven helpful in managing the symptoms of mental illness and riding the wave of alcohol cravings. Physical exercise can be optimized to improve both the physical and mental health of the person.
Conclusion
It is crucial that the connection between alcohol use disorder and schizophrenia is better understood. With misconceptions surrounding both conditions, people suffering with both often do not get the help they need. However, dual diagnosis rehabs provide the perfect opportunity for these conditions to be treated with an integrated approach.